As I mentioned in my last post, two things we can now be sure the internet will deliver up at Easter are rehashes of the tedious "Jesus never existed" thesis and memes telling us that "Easter is actually pagan!". The one above has become one of the most popular in recent years, so much so that its "Ishtar = Easter" claim has taken on internet factoid status. More recently, online New Atheists seem to have finally worked out that the "Ishtar" claims are New Age garbage, so they now prefer ones like these:
 |
| From the 'No More Make Believe' Facebook group |
 |
| From the 'Philosophical Atheism' Facebook group |
Ishtar and Easter
Back in 2013 someone posted the "Ishtar = Easter" meme on the Richard Dawkins Foundation for Reason and Science's Facebook page. Around the same time someone noted this on the Richard Dawkins Foundation for Reason and Science site, posted a link to a Scientific American article that made a rather poor attempt at debunking the meme, and then they actually made a smart point:
"There have been many of these types of ideas spreading around through documentaries & books these days. Many of them seek to connect Christian traditions with pagan ones. I must say, I can understand the reasons behind the claims: However, there still has to be historical proof to back such claims."
Fact-checking using evidence? What a great idea. Unfortunately the 25 responses the post received displayed little to no sceptical analysis, let alone any actual reference to source material or evidence. Most of the comments simply droned on about how the idea was "highly plausible" or some general comments about how "Christians adopted many pagan practices and beliefs". There were also some even more crackpot contributions, such as the guy who doubles down and says Easter is not derived from Ishtar ... but from the goddess Isis! There was one lonely comment from someone who actually bothered to do "some simple Googling" and managed to work out that Easter and "Ishtar" have nothing to do with each other, however he got completely ignored. So much for fact checking by the fans of the so-called "Foundation for Reason and Science".
Let's take the claims in the meme one by one:
"Ishtar is pronounced 'Easter'"
No, it isn't. In modern English, it's pronounced the way it looks, with "Ish-" as the first syllable. The original Akkadian name is 𒀭𒈹 
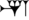 , which is transliterated as D-IŠTAR (the first letter here is "dingir", which indictes that this is a deity's name), so this was probably pronounced "ISH-tar" or perhaps "EESH-tar", but not "EAST-er". Any similarity between the way the modern English form "Ishtar" looks and the modern English word "Easter" sounds is purely co-incidental.
, which is transliterated as D-IŠTAR (the first letter here is "dingir", which indictes that this is a deity's name), so this was probably pronounced "ISH-tar" or perhaps "EESH-tar", but not "EAST-er". Any similarity between the way the modern English form "Ishtar" looks and the modern English word "Easter" sounds is purely co-incidental.
"Easter is originally the celebration of Ishtar, the Assyrian and Babylonian goddess of fertility and sex."
Contrary to popular opinion, the idea that ancient deities were somehow the gods or goddesses "of" simple, particular things is far too simplistic. Ishtar was the Akkadian counterpart to the Semitic goddess Astarte and came to be identified with the Sumerian goddess Inanna. Inanna had some associations with fertility - she was associated with the date palm and with wool, meat and grain. There is some evidence that Ishtar's cult involved sacred prostitution, though this is disputed, since it comes from a very late account by Herodotus. She had several lovers, but a clear indication that she was any kind of "goddess of sex" is hard to establish. This element seems to get emphasis in the meme because the idea that Easter was "originally about fertility and sex" rather than anything boring and Christian is much more fun to believe.
"Her symbols (like the egg and the bunny) were and still are fertility and sex symbols (or did you actually think eggs and bunnies had anything to do with the resurrection?)."
Ishtar was associated with several symbols, but "the egg and the bunny" are not among them. Her symbols seem to have been the star, usually with eight points, often alongside a crescent moon or a rayed sun or both, the lion and the gate.
"After Constantine decided to Christianize the Roman Empire, Easter was changed to represent Jesus."
This sentence doesn't make much sense on two levels. Firstly, Constantine did not decide "to Christianize the Roman Empire". He converted to Christianity in 312 (or maybe just came out openly as Christian then) and in 313 he decreed toleration of all religions, ending the periodic persecution of Christianity in the Empire. Despite this, he did not embark on any campaign to impose Christianity on the Empire and, at least initially, took an outwardly neutral path on religion so as not to alienate the still largely pagan senatorial and equestrian classes on which he depended for his administration. Later, he passed edicts that ended most state sponsorship of the pagan cults and sought to limit public pagan worship, though it's unclear how rigidly the latter were enforced. The conversion of the emperor and his family to Christianity and, more importantly, the removal of massive imperial funding of pagan temples and centres certainly did have the effect of greatly increasing conversions to Christianity over Constantine's reign and that of his successors, but the Empire was not "Christianised" until the reign of Theodosius, who made Christianity the state religion in 380 AD; 43 years after Constantine died.
The only connection between Constantine and Easter is his calling of the First Council of Nicea in 325 AD, with the aim of settling several disputes within the Christian churches. While the primary issue for the Council was sorting out the Arian Controversy over the nature of the Trinity, the Council also ruled on when Easter should be celebrated. This issue had been controversial within Christianity for some time, with Eusebius reporting that as early as 190 AD there had been disputes about whether the celebration of the resurrection of Jesus should be celebrated in line with the Jewish Passover or only on a Sunday, since Jesus is reported to have risen from the dead on the Sunday after his crucifixion. Most Christians in the west of the Empire celebrated the Resurrection on a Sunday but in the east many churches kept in sync with the Jewish Passover, with the relevant day often falling on a weekday as a result. So the Council of Nicea ruled that it should always be celebrated on a Sunday and seems to have ordered that it should fall on the Sunday following the first full moon after March 21.
Obviously the fact that Christians were having a dispute about when Easter should be celebrated indicates that there was already a celebration of Easter long before Constantine, so the claim that somehow "Easter was changed to represent Jesus" (whatever the hell that means) is clearly garbage. And the only reason their celebrations of Easter were connected to the vernal equinox is because that is the time of the Jewish Passover and Jesus was said to have been executed around Passover. So the date has a purely Christian origin that has nothing at all to do with pagan festivals (though Passover may have had a prehistoric origin in some kind of Semitic spring festival). Finally, there is no evidence of any association between Ishtar and the vernal equinox, let alone the Sunday following the first full moon after March 21.
Those who peddle this stupid New Age "Ishtar = Easter" meme also don't explain how the word somehow jumped all the way from the Middle East to England, skipping pretty much every single other Christian nation on the way. This is why, despite the fact the festival is called "Easter" in the English speaking world, in almost every other European language it is some variant on the Greek Πάσχα:
French: Pâques; Romanian: Paşti; Portugese: Páscoa; Italian: Pasqua; Spanish: Pascua; Faeroese: Páskir; Swedish: Påsk; Icelandic: Páskar; Welsh: Pasg; Norwegian: Påske; Danish: Påske; Dutch: Pasen; Russia: Paskha.
Πάσχα in turn is derived from the Hebrew פֶּסַח (Pesach) meaning ... Passover. Only an idiot could look at this and somehow conclude that the English word "Easter" had anything at all to do with the name of an ancient Akkadian goddess who was worshipped two millennia before the first English speakers and 4,000 kilometres to the south east of England. But there are a lot of idiots on the internet and, unfortunately, it seems some of them are associated with the Richard Dawkins Foundation for Reason and Science.
 |
| The goddess Eostre, according to some neo-pagan hippy on Pinterest |
So How About the Goddess Eostre?
If Easter has nothing to do with Ishtar, what about the claims about it coming from "the pagan goddess Eostre"? We are told that this is the "real" origin of Easter in other memes propagated uncritically by online New Atheists. Apparently she was a "pagan goddess of light and fertility" and a "Spring Goddess" who "breathed life back into the world". Lots of online sources seem to know a great deal about her and tell us that she was associated with hares and rabbits ("thus the Easter Bunny, see?") and eggs ("fertility symbols that have nothing to do with silly old Christianity!"). These things are all asserted with the internet's usually breathless assurance and so it all seems perfectly clear that "Easter" was originally this pagan goddess' spring fertility festival. Unless you bother to actually check on the sources of all these claims and find this is not clear at all. In fact, it's actually highly uncertain.
To begin with, we have the grand total of one reference to any pagan goddess called Eostre, and it's pretty dubious. It's actually found in an early medieval Christian work focused on that vexed issue of the calculation of the date of Easter. In 725 AD the prolific English monk and scholar Bede wrote De temporum ratione or "The Reckoning of Time" to help monks calculate Easter, but in the process he detailed various calendrical schemes, gave a potted history of the earth and, thanks to the work's popularity, helped fix the BC/AD dating scheme as the standard. In his discussion of calendars he gives us the traditional Old English names for the months, with a brief discussion of each. Some of his etymologies seem to refer to the agricultural cycles of the year, such as Weodmonath (August) or "weed month" or Thrimilcemonath (May) "three milkings month" so called because in that month cattle were milked three times a day thanks to lush spring grass. Others refer to pagan practices. Bede says Halgemonath (September) is "Holy Month" because it was a "month of sacred rites", possibly associated with harvest. And he says two months were named after goddesses - Hrethmonath (March) after Hrêða and Eostremonath (April) after our Eostre:
"Eostremonath has a name which is now translated Paschal month, and which was once called after a goddess of theirs named Eostre, in whose honour feasts were celebrated in that month. Now they designate that Paschal season by her name, calling the joys of the new rite by the time-honoured name of the old observance." (Bede, De temporum ratione, XV)
That would seem to settle it - here is an early medieval source telling us that the month in which Easter (usually) falls was named after a pagan goddess called Eostre, so the festival is pagan. Except things aren't quite that simple.
We have no other references to this "Eostre" anywhere in any other source. Our sources of information on early Germanic mythology are scanty and fragmentary, but it is odd for us to have just one reference to a deity and no other indication of their worship: no references to her in other Christian sources, no inscriptions, no charms mentioning her name, no place names indicating her cult sites and no cognates of her name in later Old Norse texts on the Viking gods. Bede was writing in the early eighth century and a couple of generations after England had converted to Christianity. Even then many pagan practices and ideas would still have survived, but how familiar with them a devout monk living in the monastery of Jarrow would have been is not clear. The lack of any other references to this goddess is suspicious and there is a very good chance Bede didn't have a clue what "Eostremonath" meant and that he invented an "Eostre" goddess to explain the obscure name.
The month name was not only found in England, however, and the prolific nineteenth century philologist Jakob Grimm (of Grimm's Fairy Tales fame) noted that in his day some Germans still called April "ostermonat". He also pointed to the Old High German version of the same month name: "ôstarmânoth" and the recorded Old High German words for two festival days: "ôstartagâ" and "aostortagâ". He concluded from this that Bede must have been right and that a feast of "Eostre" or "Ostara" must have been held at this time.
Grimm was very good, however, at finding Germanic gods and festivals in the most fragmentary and obscure of evidence and while the Old High German cognates for the month name and festival days may indicate something pre-Christian, they don't necessary add up to a goddess. The very cautious modern scholar of all things pagan, Ronald Hutton, accepts that Bede and Grimm may have been right, but we can't be very sure:
"[T]he Anglo-Saxon eastre, signifying both the festival and the season of spring, is associated with a set of words in various Indo-European languages,signifying dawn and also goddesses who personified that event, such as the Greek Eos, the Roman Aurora, and the Indian Ushas. It is therefore quite possible to argue that Bede’s Eostre was a German dawn-deity who was venerated at this season of opening and new beginnings. It is equally valid, however, to suggest that the Anglo-Saxon “Estor-monath” simply meant “the month of opening”, or the “month of beginning”, and that Bede mistakenly connected it with a goddess who either never existed at all, or was never associated with a particular season, but merely, like Eos and Aurora, with the Dawn itself.” (Hutton, Stations Of The Sun, p.180)
The etymology seems to trace back to the Indo-European root "*aus-" meaning "to shine" which in turn is the root for the modern English word "east" and a range of cognates referring to "the dawn", to "shining" and to the "sun". So "Eostremonath" could refer to an otherwise totally unattested goddess, a goddess not associated with Easter or it could be a reference to the month when the sun shines again as winter gives way to spring. We simply don't know.
 |
| More neo-pagan New Age fantasy |
Rabbits, Hares and Eggs?
So Easter has nothing at all to do with Ishtar and Eostre may not even have existed. What about the pagan remnants that are Easter eggs and the Easter Bunny? As already noted above, there is no evidence linking Ishtar to eggs, rabbits or hares, despite the claims to that effect. And if we can't even be sure if there was an Eostre, clearly we have no information about her being connected to eggs or bunnies if she existed.
Given that no eggs or rabbits appear in any of the Easter narratives in the gospels, most people assume they have to have pagan origins. After all, the usual Christian explanation that the eggs "symbolise the rebirth of Christ at his Resurrection" sounded dubious to me even as a child. But it seems that the tradition of decorating and eating eggs at Easter does have a medieval Christian origin after all.
Christianity has long instituted days of fasting in association with various festivals and celebrations in its liturgical calendar and the earliest evidence we have of a 40 day fast before Easter comes in the festal letter of Athanasius from 330 AD. What a "fast" meant varied, but it usually involved abstaining from meat and often also required avoiding all animal food products, including cheese, butter and eggs. The fifth century historian Socrates Scholasticus noted at least some people abstained from eating eggs on fast days and the Council in Trullo in 692 AD recommended that people do so:
"It seems good therefore that the whole Church of God which is in all the world should follow one rule and keep the fast perfectly, and as they abstain from everything which is killed, so also should they from eggs and cheese, which are the fruit and produce of those animals from which we abstain."
By the Middle Ages, abstaining from eggs on fast days and in Lent had become the standard practice in western Europe. Thomas Aquinas made this requirement perfectly clear:
"Eggs and milk foods are forbidden to those who fast, for as much as they originate from animals that provide us with flesh … Again the Lenten fast is the most solemn of all, both because it is kept in imitation of Christ, and because it disposes us to celebrate devoutly the mysteries of our redemption. For this reason the eating of flesh meat is forbidden in every fast, while the Lenten fast lays a general prohibition even on eggs and milk foods." (Summa Theologica, II.2. 127)
So this prohibition gave rise to two European customs maintained to this day: eating pancakes and pastries on "Shrove Tuesday" before the Lent fast began and eating eggs on Easter Sunday when it ended. Using up what eggs, milk and butter people had before the fast made sense rather than letting this perishable food go to waste. And since hens would be paying no attention to any fasts and still laying through Lent, there would have been plenty of eggs on hand to eat on Easter Sunday morning. In fact, eggs gathered in the week ahead of Easter could have been stored or hard boiled in preparation for Easter Sunday morning, when they would have been quite a treat to peasants who had just endured over a month on a diet of bread, vegetables and some fish.
We have the first references to these eggs being decorated in the thirteenth century, but that practice may have started earlier. What we don't have is any reference to any pagan spring festival or customs involving eggs. The most logical source of Easter eggs, therefore, is the Christian practice of a Lenten fast in which this readily available staple could not be eaten.
The "Easter Bunny" is a modern commercial take on the northern European association of hares (not rabbits) with Easter. Again, there is no evidence of any pagan origin here. Hares are generally shy and solitary animals, but in early spring they become more social as part of their mating behaviour. So around March in most of northern Europe hares can be seen in the fields "boxing" - with males competing for mates and females occasionally rebuffing males physically. The sight of groups of hares in the fields would have been a sign of the onset of spring and that Easter was around the corner for rural people without calendars, thus the German and Dutch tradition of the "Easter Hare" which came to the US and became the "Easter Bunny". So, again, no paganism.
Where Does All this Crap Come From?
So Ishtar had nothing to do with Easter, Eostre may not have even existed and Easter eggs and the Easter Bunny aren't pagan either. So where did all this crap come from? One of the interesting things about having spent several decades tracking down crank pseudo history is how often I find these dumb ideas can all be traced back to single sources. In this case we have memes being shared uncritically both by New Agers and neo-pagans and by vehement New Atheists. Which is deeply ironic, given that the source of these memes seems to be a nineteenth century fundamentalist Christian minister.
Alexander Hislop (1807-1865) was a minister in the Free Church of Scotland and parish schoolmaster in Caithness. He was a vehement critic of anything to do with Catholicism and became convinced that while good Protestants like him followed the true faith of Jesus Christ, the Catholic Church was actually the ancient Babylonian mystery cult of Nimrod, an obscure pagan figure mentioned a few times in the Old Testament. According to Hislop, Satan allowed the Emperor Constantine (him again) to hijack the true Christian faith and lead it into idol-worship and Papist errors and that it was only by recognising this and throwing off any pre-Reformation vestiges that people could return to true Christianity.
Hislop initially published this thesis as a pamphlet in 1853, but then added a large amount of material to it and published it as The Two Babylons: The Papal Worship Proved to Be the Worship of Nimrod and His Wife in 1858. Hislop's book is a remarkable case study in the level of abject nonsense that can be created out of a stupid initial assumption, a burning desire to find (or create) evidence to support it and the motivating energy of good old fashioned bigotry. So Hislop takes sources that have since been shown to be wrong and new information from digs in the Middle East that he didn't understand to create a fantasy of stunning complexity and idiocy. We are told that the mitres worn by Catholic bishops take their shape from the "fish head hats" worn by the ancient priests of the god Dagon, though this ignores the fact that Catholic mitres didn't take their current form until at least the tenth century and earlier forms didn't look anything like the bizarre hats in Hislop's dubious illustrations of these pagan priests. And where Hislop was unable to come up with evidence he simply makes strings of assertions, like "Nimrod was born on December 25" or "Christmas tree baubles are Babylonian sun symbols" - none of which have the slightest substantiation.
Not surprisingly, Hislop's book became a best-seller and remains very popular among the loonier elements of fundamentalist Protestantism. The Jehovah's Witnesses still cite Hislop as an august authority in regular articles repeating his claims. The infamous tract publisher Jack T. Chick was a huge fan of Hislop and several of his crazier evangelical comic books were simply rehashes of Hislop's thesis (such as his 1987 comic "Why is Mary Crying?"). And white supremacist groups of the "Christian Identity" variety also regularly feature Hislop's claims in their material.
Hislop seems to be the ultimate point of origin for the claims that Ishtar and Eostre were the original source of Easter, thanks to the wickedness of Catholics and, of course, Satan. He devotes a whole section to the pagan origins of Easter in his chapter on the wicked Satanic festivals of the Catholic Church:
"What means the term Easter itself? It is not a Christian name. It bears its Chaldean origin on its very forehead. Easter is nothing else than Astarte, one of the titles of Beltis, the queen of heaven, whose name,… as found by Layard on the Assyrian monuments, is Ishtar ..." (Hislop, p. 103)
He goes on to detail a fervid fantasy about Middle Eastern gods being taken to Britain by, of course, the Druids, who he claims worshipped the Babylonian god Baal. Then he makes the following series of leaps:
"If Baal was thus worshipped in Britain, it will not be difficult to believe that his consort, Astarte, was also worshipped by our ancestors, whose name in Nineveh was Ishtar. The religious solemnities of April, as now practised, are called by the name of Easter - that month, among our Pagan ancestors having been called Easter-monath." (Hislop, p. 104)
He then traces this pagan Easter and its Catholic customs via a circuitous route via the 40 day fast of "the Yezidis, the Pagan Devil-worshippers of Koordistan" and, somehow, the "Pagan Mexicans" and the cults of Adonis, Osiris, Ceres and Tammuz before it was imposed on the poor Christians of Britain by the wicked and Satanic Church of Rome. He concludes:
"Such is the history of Easter. The popular observances that still attend the period of its celebration amply confirm the testimony of history as to its Babylonian character. The hot cross buns of Good Friday, and the dyed eggs of Pasch or Easter Sunday, figured in the Chaldean rites just as they do now." (p. 107-08)
Pretty much all the elements of the memes above can be found here, though not the Satanic hot cross buns, which Hislop condemns as celebrating "the goddess Easter" and therefore also evil. I imagine Mr Hislop was not much fun at parties.
Hislop's junk scholarship was very popular and while his whole thesis generally only appealed to his hardline Protestant audience, his claims permeated nineteenth and early twentieth century culture. So we can find them popping up in esoterica, in tracts by Theosophists and occultists and in Freethinker pamphlets, which recycled anti-Catholic material with uncritical enthusiasm. And now we find the supposedly "rational" New Atheists of the Richard Dawkins Foundation for Reason and Science and the the "No More Make Believe" and "Philosophical Atheism" Facebook groups cluelessly regurgitating this hoary fundamentalist Christian nonsense because they don't check their facts and just take any nonsense that appeals to them on ... faith. Oh, the irony.
Update - April 19 2017: In a great victory for rationalism, I have now been blocked by the the "No More Make Believe" Facebook group. I suppose that's one way of dealing with pesky people who point out their errors of fact.



Comical, isn't it, that the same people who cling to Jesus mythicism ("there's not enough evidence to prove he existed") will carry the Oestre fable to their graves based on a single reference by Bede?
ReplyDeleteOne sentence by Bede? QED!
Hi Tim, thanks for doing all that research. The end result of all this imagination would be somewhat amusing if it wasn't taken so seriously by some.
ReplyDeleteI think there is one level where christianity may have been influenced by paganism, in a way. In England at least, and quite possibly elsewhere, christians appear to have "christianised" sites and seasons that were sacred to pagans. So the date of Christmas, nowhere mentioned in any reliable historical documents I have seen in reference to Jesus' birth, was likely used to commemorate his birth to christianise a pagan festival. Likewise churches were sometimes built on sites that had pagan meaning. At least, I think these things are so - do you know?
As a christian, I have no problem with any of that - after all, if I was worried about that, how would I live on Marsday, and Tyrsday, or Wodensday or Thorsday or Freyasday? And as a christian, I would be very happy if easter eggs and bunnies were pagan in origin - I don't really like the way they have become so commercialised, appearing in our local supermarket immediately after the Christmas junk goes on half price sale in January. But it is good to have some well researched information. Thanks.
"In England at least, and quite possibly elsewhere, christians appear to have "christianised" sites and seasons that were sacred to pagans."
DeleteThere's absolutely no doubt about that. Many churches are built on top of or out of or even inside of older cultic centres and sites. A lot of saints' days are former pagan festivals and a few saints (Christopher, Brigid) are simply rebadged pagan deities. And many former customs were retained and simply lost most or all of their former associations. So we still put up Christmas trees and the good people of Abbots Bromley still take the 1000 year old reindeer antlers from their parish church and dance around with them each September centuries after everyone has forgotten why.
And we know that a lot of this was a deliberate conversion policy, as evidenced by sources like Gregory the Great's instructions to Bishop Mellitus in 601 AD. But this doesn't mean that every folk tradition or obscure practice has some pagan origin. Unfortunately a lot of the older breed of anthropologists and folklorists found gods and pagan cults under every toadstool and any vague parallel somehow had to be a derivation.
"So the date of Christmas, nowhere mentioned in any reliable historical documents I have seen in reference to Jesus' birth, was likely used to commemorate his birth to christianise a pagan festival."
Ummm, no actually. See my post on that subject: "The Great Myths 2: Christmas, Mithras and Paganism".
"But it is good to have some well researched information. Thanks."
You're very welcome. Of course, I'm fighting even more of an uphill battle against this crap than on most of the topics I tackle here.
It's a thankless task to have to correct not only the internet atheists, but also the hidebound fundamentalist Protestants, who are so wedded to this rubbish, but thank you for doing so.
ReplyDeleteRegards
Jason
I've been attacked as a wicked close-minded atheist by both hardline Catholics and Protestants, as a Christian apologist by New Atheists and as a crypto-Catholic by both New Atheists and fundamentalist Protestants. All these insults from the crazies can get confusing.
DeleteChesterton did observe something along the lines that, "if everyone else is saying you're crooked, maybe you're the only straight person in the place."
DeleteHi Tim, thanks for that correction. I remember reading it when you first posted it, but I had forgotten that part.
ReplyDeleteI just want to say, Tim, that you're the best.
ReplyDeleteAlso, re: above, "Unfortunately a lot of the older breed of anthropologists and folklorists found gods and pagan cults under every toadstool", I'm reminded of the saying that when an anthropologist says that something had a symbolic ritual meaning, it means that the anthropologist doesn't understand what it was actually about. (And this is from the anthropologists themselves, not dissing them.)
Tim, you are transforming my life. :-) I am former atheist with Slavic background, and I was always uneasy about the traditions we have around eggs. Slavs decorate them elaborately on Thursday before Easter. Even much of our secular art was profoundly influenced by egg imagery (look up Faberge Eggs - they are stunning). You are reconnecting me back to my civilization's roots - eggs are "kosher" and fun, my family will employ them in celebration every year from now on. Much gratitude to you!
ReplyDeleteI will see your Faberge eggs and raise you pysanky -- Ukrainian-style Easter eggs dyed with a wax-resist method in successively darker dye-baths. The technique is not dissimilar to the "batik" method of fabric dyeing, and the resulting designs can be stunningly complex.
DeleteAnyway, regarding the origins of the Easter egg, I'm very reluctant to give up the "pagan fertility symbol" theory, because:
(1) The function of the egg recalls the swollen womb of female mammals -- it nurtures the baby inside it.
(2) The shape of the egg suggests a mammalian testicle -- thus, it represents the masculine reproductive principle as well as the feminine reproductive principle. (I might add that the Russian noun yaitsa, literally "eggs," can be used in exactly the same rude way that we use "nuts" or "balls" in English. Anthony Burgess, in A Clockwork Orange, punningly invents the Nadsat slang word "yarbles," as in "The millicent kicked me in the yarbles, oh my bratties.")
(3) The shape of the egg ALSO suggests a human woman's breast. Google on the so-called "Diana of Ephesus" -- a famous statue in which Diana/Artemis appears to be wearing a blouse sewn out of hardboiled eggs, à la Lady Gaga, but in fact she's got about a hundred tits.
(4) The appearance of the yolk inside suggests the unconquerable solar-god, who always manages to defeat the Eclipse Dragon, and always returns after winter.
(5) Finally, eggs cooked in the shell are an essential part of the Jewish seder during Passover -- which may not be as old as Jewish tradition claims, but certainly was around long before Christian Lent. Other elements of the seder are explained as overt symbols of the Exodus story, but not eggs.
None of this proves a pagan origin for Easter eggs, but it suggests to me that the "eggs were given up for Lent" idea is not the full explanation.
Sorry, but points 1-4 only add up to a small "maybe". Even if we grant all of that potential symbolism, there is no reason to think that these associations somehow mean these associations have to be pre-Christian. Not all customs have to have a prehistoric past: people come up with new customs all the time and they can and do have both conscious and subconscious symbolic resonance.
DeletePoint 5, however, is wrong. Despite modern Jewish claims that eating eggs at Seder is an ancient custom, it is not attested anywhere until a German commentary by Rabbi Moses Isserles (1520-1572). Whereas we have references to Easter eggs being eaten (and decorated) as early as the thirteenth century. It could actually be that the Christian custom influenced the Jewish one, especially if a Lent surplus of eggs meant there were plenty of them in the markets around Passover and Easter.
Great work Tim. I've tackled the same meme here: https://www.facebook.com/ChristianOrigins/posts/818774234944539:0
ReplyDeleteThank you for this. I love a good debunking and this is the most thorough debunking of all the Easter meme nonsense that I've seen. I love that you were able to track down the source of the stories to a single guy. It's very satisfying to know where the stories come from.
ReplyDeleteDidn't Chesterton also (reportedly) say: "When people don't believe in something, then they'll believe in anything?" And also "It's all very well having an open mind, as long as it's not open at the bottom"?
ReplyDeleteThen how did the name Easter came to be attributed to the day of resurrection? Do you know? It is obviously not in any of New Testament books. What is the earliest instance where a Christian work designates the day of resurrection as Easter? What is the meaning of the term Easter? Does that word has any meaning related to resurrection?
ReplyDeleteAs I explain in the article, "Easter" is only used in English. Virtually every other European language uses some form of the word Πάσχα "Pascha", which means "Passover". Because Jesus was executed on the Jewish Passover.
DeleteBut English uses "Easter" and German uses "Ostern" because Easter falls in a month that seems to have once had a pagan festival called "Eostre" in Old English and "Ostara" in Old High German. All we can say is that English and German took on the old name for their Christian festival, while other languages retained the traditional Christian name. We have no other information about this "Eostre"/"Ostara" festival, so we simply don't know if any pagan elements from it survive in Easter traditions. But, as I detail above, Easter eggs and Easter bunnies/hares don't seem to be pagan in origin, despite all the online claims to the contrary.
Good read! Thank you!
ReplyDeleteI'm still wondering how we wound up using the term Easter when most other languages use a word rooted in or connected to Passover. Any thoughts?
See my reply to John Thomas.
DeleteIt apparently got called Easter by early English Christians because it normally took place in April, which the English called Eostremonath. Early English missionaries took that term with them when they evangelised, for example, in Germany (where their ancestors had come from). And so "Easter" seems to have stuck in English. For a similar reason the English called Pentecost "Whitsun".
Delete"Early English missionaries took that term with them when they evangelised, for example, in Germany (where their ancestors had come from).
DeleteThere were certainly Anglo-Saxon missionaries to the pagan areas of old Germania, such as Willibrord's and Willehad's missions to Frisia and the two Edwalds in Saxony and Boniface in Hesse and elsewhere.
But do you have any evidence that supports the idea that they brought the word "Eostre" with them? Because if any exists, then the Old High German "Ostara" is not am original Germanic cognate at all and the idea of a pagan Germanic "Eostre"/"Ostara" goddess and/or festival shared across the pre-Christian west Germanic world becomes much less likely than Grimm suggests.
In Eastern Christianity, this is one of the reasons we decorate eggs in our traditions. Also, we refer to Easter as "Pascha" (pas-ka), because Christ is the New Passover.
ReplyDeletehttps://orthodoxwoman.wordpress.com/2012/04/11/the-red-easter-egg/
A bit more on the Eastern Orthodox Paschal theology. :)
https://orthodoxwiki.org/Passover
Sir,
ReplyDeleteYou are doing the Lord's work. ;-)
*Chuckle* Actually, I serve only Lady Clio. But thanks.
DeleteDear Tim,
ReplyDeleteInterestingly, Easter is called Ostern in modern German and "Ost", the root word of Ostern, means east.
Strange coincidence (or Germanic conspiracy;-)?
Seriously, though, I'm uncertain what to make of this etymology.
As I note in the article, German is the only European language other than English that uses a Germanic word for "Easter", rather than a variant based on the Greek Πάσχα (Pascha). So even in the other Germanic languages we have Faeroese: Páskir; Swedish: Påsk; Icelandic: Páskar; Norwegian: Påske; Danish: Påske; Dutch: Pasen etc.
DeleteWe don't know what the etymology of "Easter" and "Ostern", but the former comes from the Old English "Eostre" and the latter from the Old High German "Ostara". As I say above, these words may refer to a goddess, or may refer to an "opening" (eg the opening of spring) or may refer somehow to "the east" and therefore the dawn. We simply don't know and can only note the possibilities. The problem lies in people - both New Agers/neo-pagans and New Atheists - who state one of them as a fact because it suits their agendas.
Thank you for your prompt answer. I apologize if my comment appears twice - I thought I accidently erased my query.
DeleteI found a comment that Steve Hayes made quite intriguing, where he poses the idea of "Early English missionaries took that term with them when they evangelised, for example, in Germany".
So I thought, maybe the etymology is more a simple case of a translation attempt rather than a complex invoking of goddess names or references to the dawn.
Yes, no, maybe?
That would be a very big "maybe", unless I see some evidence to support that claim. As I note in my reply to Steve, it's true that there were Anglo-Saxon Christian missions into pagan continental Germania, so it's possible that the Old English word was taken over with these missionaries. But I would need to see some solid evidence for this. I asked him if he had any and he's not replied yet. I suspect he doesn't.
DeleteAccording to the German Wikipedia etymology for Ostern, there are regional differences in how the holiday has traditionally been referred to.
DeleteThe more southerly arch diocese of Cologne with its Frankish-German called it pāsche, while the bishop's seat of the more northerly Mainz region favored the use of the anglo-saxon term "ostarun", meaning "morning red" or "dawn".
de.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ostern#Etymologie
Perhaps this north-south differentiation can be due to the influence of English missionaries, who most likely would have approached Germany from the north?
That's possible. But far from certain.
DeleteJust a small note, German is not the only European language not to have a Pascha variant. Estonian doesn't either. In Estonian it's an expression indicating the end of fasting: lihavõtted, "meat/flesh-taking". There's also an expression which just means "resurrection feast". But no expression derived from Pascha. NOR from Easter.
DeleteBy chance, is anyone here a native German speaker, or know one? Preferably a German speaker who's had some technical linguistic training in the development of proto-Germanic dialects in the 1st millennium AD. Here's why I ask:
ReplyDeleteI recall reading somewhere the suggestion that the word "Easter" does NOT come from the Germanic noun root _oest_ ("the dawn" or "the east") with a SUFFIX added to it, but rather the Germanic verb root _stehren_ ("to stand") with a PREFIX added.
In support of this conjecture:
(1) Early Greek-speaking Christians would've used the word anastasis is used in reference to Jesus's resurrection -- the -stasis part implies "the act of standing", while the ana- prefix can signify either "upward" or "again," depending on context. As Christianity spread, it would've been natural to render unfamiliar Greek theological terms with a root-for-root "calque" translation.
(2) In modern German, or so says Google Translate, the verb "to resurrect" is auferstehen -- i.e., a prefixed form of the basic verb that means "to stand." Chop off the auf- part and what's left is not too far phonetically from "Easter."
All this sounds plausible -- but I don't know nearly enough about German to guess whether it's actually true! On the other hand, I know enough about languages in general to be aware that totally logical-sounding etymologies often turn out to be bogus.
I think the main problem with that idea would be the attestation of Bede for the Old English traditional month name of "Eostremonath", which has the Old High German cognate of "ostermonat" and the festival names "ôstartagâ" and "aostortagâ". All this evidence indicates a pre-Christian origin for the name. it just doesn't necessarily indicate a pre-Christian goddess.
DeleteThere's literally 0 evidence associating Ishtar with 'sacred prostitution' because the latter is a made up Victorian concept.
ReplyDeleteHerodotus' reference is about Mylitta, a different Mesopotamian goddess. Ishtar was (like Isis in Egyptian tradition) synchretized with most goddesses in the fertile crescent to various degrees but synchretism is not equivalence. Herodotus also doesn't describe 'prostitution' in the technical sense. Mylitta appears to be a Assyrian equivalent to the Sumerian Ninlil/Sud. In Akkadian times, Ishtar took over Ninlil's role to a large degree but the Akkadians wrote down lists of deity equivalencies and Ishtar is clearly stated to be the same as Inanna and several other deities she is simply not stated to be equivalent to Ninlil or Mylitta. The situation is incredibly complicated, hymns to one goddess will steal titles and copy language used to praise another goddess, early scholars (probably inspired by contemporary Hinduism) created a simpler picture by cherry picking the evidence that seemed to confirm what they expected to see. Male deities similarly steal titles and poetic phrases from each other all the time but scholars are much quicker to stuff every goddess into one 'divine feminine' than they are to argue that the god of wisdom is actually an aspect of the hero deity. Any actual understanding of ancient paganism requires one to avoid any simplifications and accept that the beliefs of ancient people were confusing and contradictory, at least from a modern perspective.
Even today if you go the British Museum you find the name "Astarte" labeling any random Near Eastern figurine. Since it was impossible to identify the represented goddess in many cases, early archaeologists just assumed that there was only one goddess and used Ishtar/Astarte as a generic label and then used the labels as evidence that the people of the ancient near east only had one goddess who was worshiped in different aspects.
The whole concept of a 'fertility goddess' is a Victorian invention based on their ideas of cultural evolution. The basic idea is Protestant with stoic influenced prudishness is the height of evolution so sex obsessed polytheism is the lowest form of evolution. Much of the evidence came from the original prudish stoics; the Roman sources that portrayed all bad rulers and foreigners as being unable to control their sexual appetites except even the Romans never mentioned actual pagan sex rites (the word orgy comes from Greek mystery cults but the word had no sexual connotations in the classical world).
There's an Akkadian word 'harimtu' that is often translated as 'Sacred Prostitute' but in no ancient text is a harimtu ever paid for sex or associated with any religious function. But in Victorian times any loose woman was a whore so they just made the translation up and it remains in encyclopedia articles to this day.
While the notion that the worship of Inanna/Ishtar/Astarte involved ritual orgies may have been a later misunderstanding, Ishtar's randiness is well established in the Sumerian/Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh. In fact, her insatiability plays a key role in the plot.
ReplyDeleteThe goddess Ishtar falls head over heels in love with the mighty demigod-king Gilgamesh, who tells her to get lost. In essence, he says that she's a total slut, but NOT one of those adorable sluts with a heart of gold, like Shamhat the temple-harlot (whose name apparently implies "she who plies her trade at the house of Shamash, the sun-god").
No, says Gilgamesh, Ishtar is a spiteful, selfish slut of the worst sort, and every one of her countless male lovers has come to grief after she got tired of him. Gravely insulted, she stomps off to daddy (one of the chief gods) and demands Gilgamesh's head.
Her father's reply boils down to: "Ishtar, sweetie, let's face it -- you ARE a colossal slut. One cannot fault the King of Uruk for merely pointing what everyone, everywhere, ALREADY KNOWS. Besides which, it's not yet Gilgamesh's appointed time to die, so what can I do?"
This sends Ishtar into full-blown Veruca Salt mode, and her insufferable whining eventually persuades the other gods to punish Gilgamesh indirectly -- by slaying his best friend, the hairy-bodied wild man Enkidu. Enkidu's death about halfway through the epic then sets things in motion for the second half.
note all the citified innovations with which they try to divert Enkidu--gold, beer, hookers, lying
DeleteYou forgot BBQ among the civilized temptations that Enkidu faces. But you're right -- when Enkidu is dying and in a fever-delirium, he at first irrationally blames the temple-harlot for his predicament, and heaps nasty curses upon her. But then the sun-god Shamash rebukes Enkidu: "If not for the temple-harlot, you would never have learned to enjoy beer and cooked meat! Plus you would have never been dressed in the robes of a prince and dined at the table of King Gilgamesh, etc." So Enkidu retracts his curses and blesses the temple-harlot instead: "May her beauty be forever famous! May all of her clients be excellent tippers! May she have a long and comfortable retirement!"
DeleteTwo questions for Tim:
ReplyDelete1. How do you decide what posts get the "Great Myths" designation?
2. You've touched on the alleged pagan origins of Christmas and Easter. Do you think you might ever cover whether or not Halloween was originally Samhain?
There are some bits of pseudo history, such as the claims about Eostre and Easter etc above, that I only see repeated by New Atheists occasionally. There are others, however, that are constantly repeated, several of which form key elements of New Atheist pseudo historiography. They are the ones I'm focusing on in the "Great Myths" series of posts.
DeleteI haven't considered an article on Halloween/Samhain because, as far as I can see, the connection between the two is pretty clear and uncontroversial.